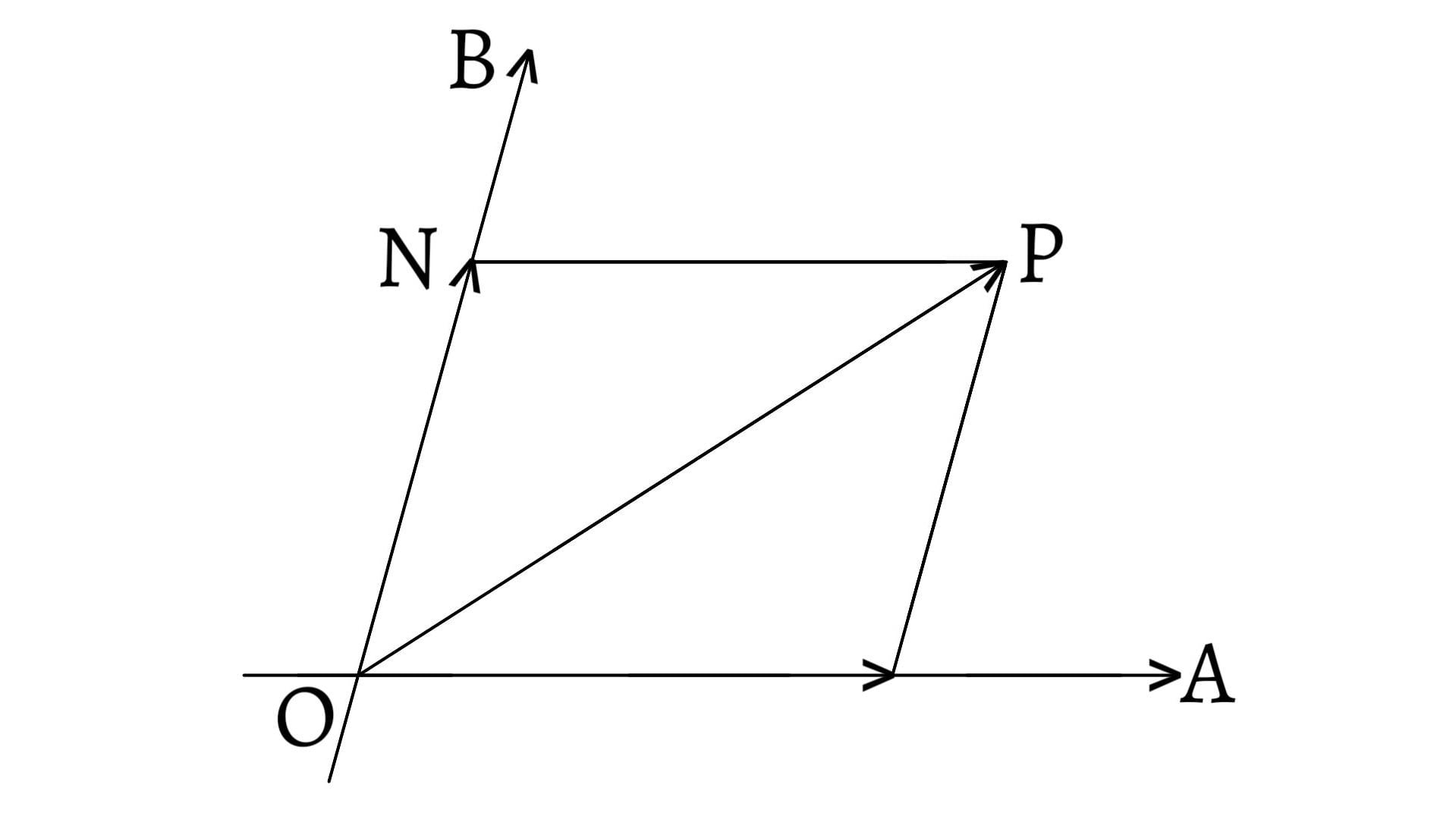
Polygon law of vectors states that if a particle simultaneously possesses a number of vectors which are represented in magnitude and direction by the sides of a polygon taken in order, then their resultant vector is represented both in magnitude and direction by the closing side of the polygon taken in opposite order.
Consider a particle
Draw a vector
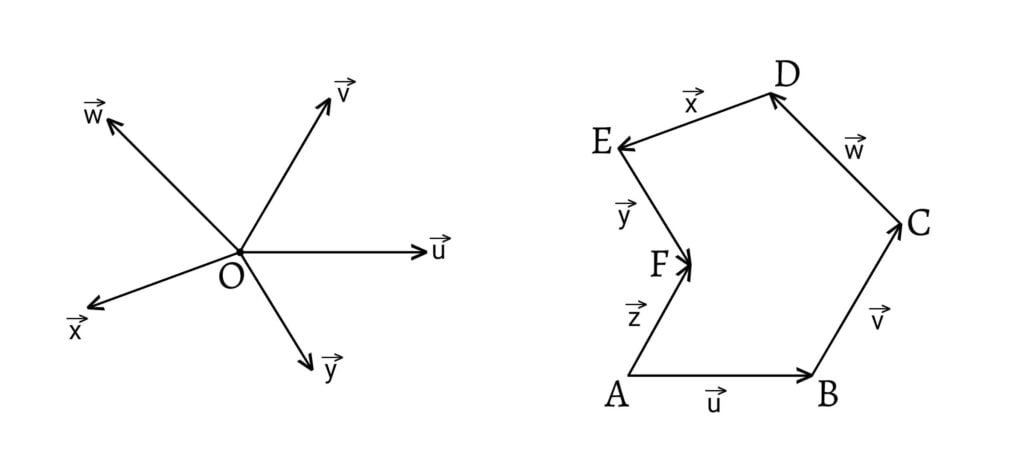
Now, join
If the particle possesses a number of vectors which can be represented in magnitude and direction by the sides of a closed polygon taken in order then the particle is in equilibrium state.
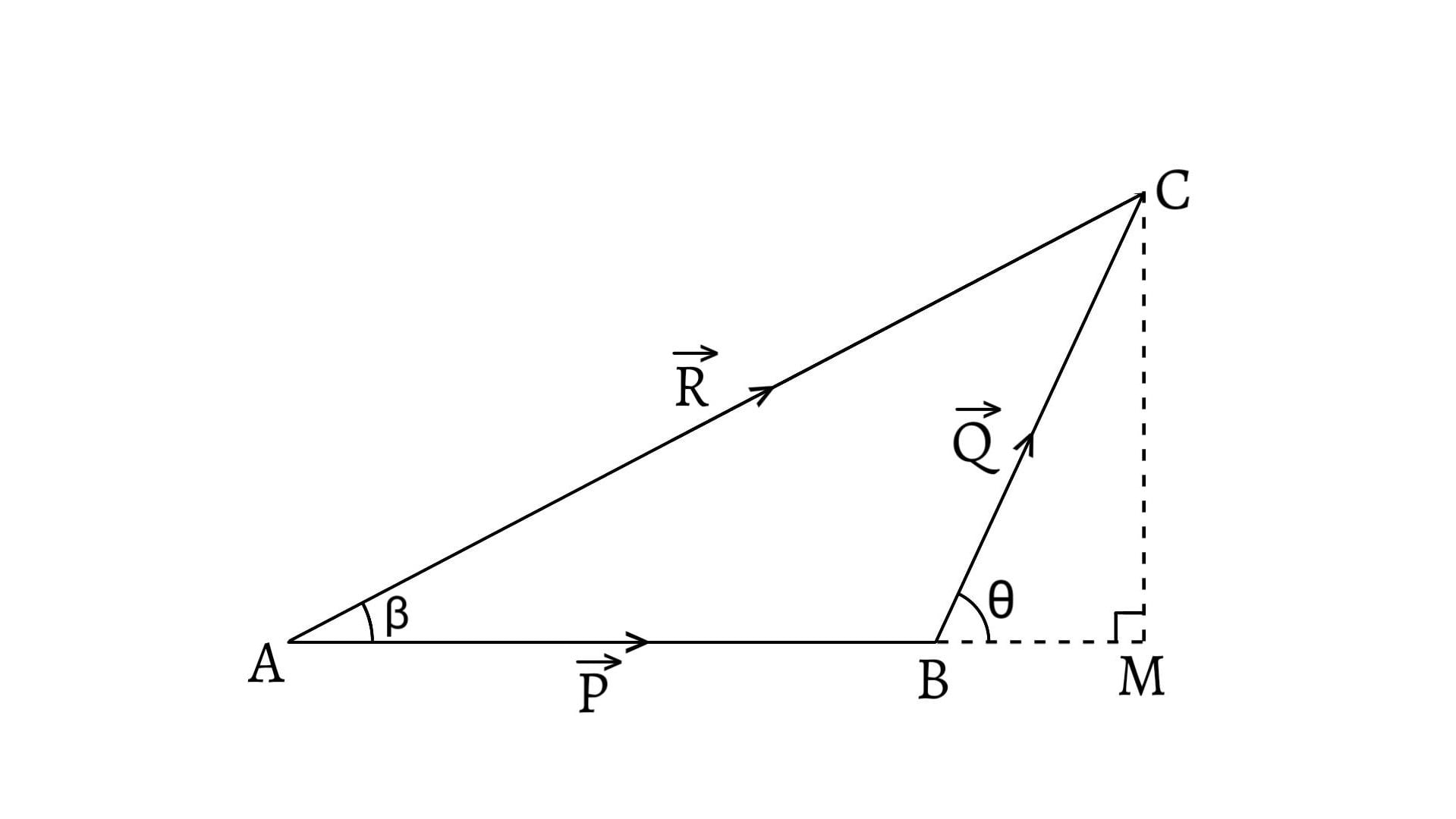
Represent the vectors

We know that the resultant of
Hence, the result of
Previous: Triangle Law of Vector Addition
Next: Resolution of a Vector