Variation of g due to the shape of the earth

We know,
Value of
Value of
For the mean value of acceleration due to gravity on the surface of the earth,
Thus, the mean value of the acceleration due to gravity on the surface of the earth is
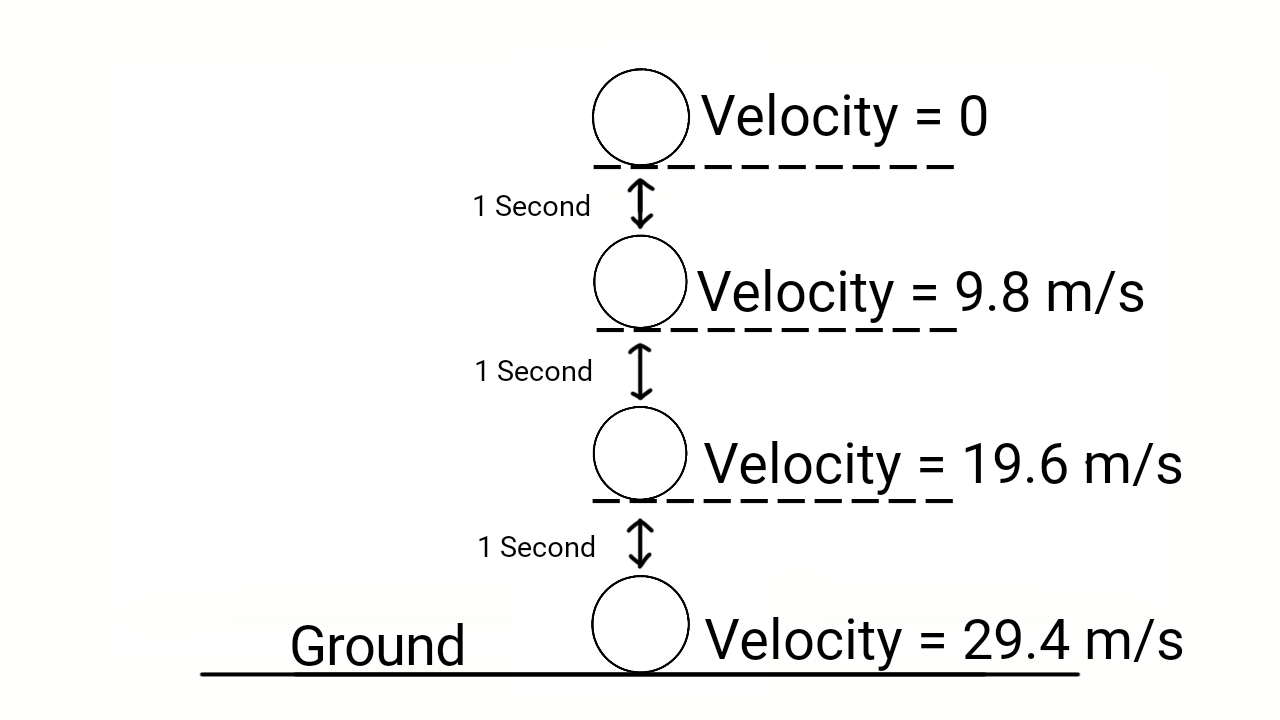
We have learnt that the acceleration due to gravity is more at the poles than at the equator. That’s why, the weight of a body is more at the poles than at the equator. And, if we dropped an object once at the equatorial regions and then at the polar regions from the same height, then that object will fall faster at the polar regions than the equatorial regions.
Variation of g due to the height from the surface of the earth
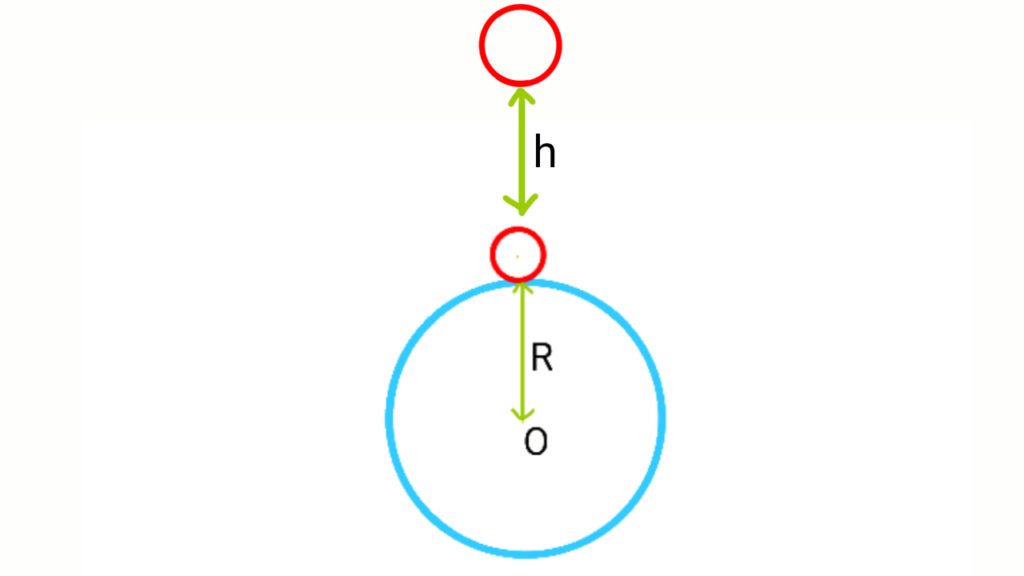
Let the mass and the radius of the earth be
Let the another acceleration due to gravity at a height
Dividing equation
Here,
Therefore, if height increases the value of the acceleration due to gravity decreases. That’s why, the weight of the body decreases as we go in higher altitude. And a body will weigh more at the sea level than at the top of the mountain.
Variation of g due to the depth from the surface of the earth
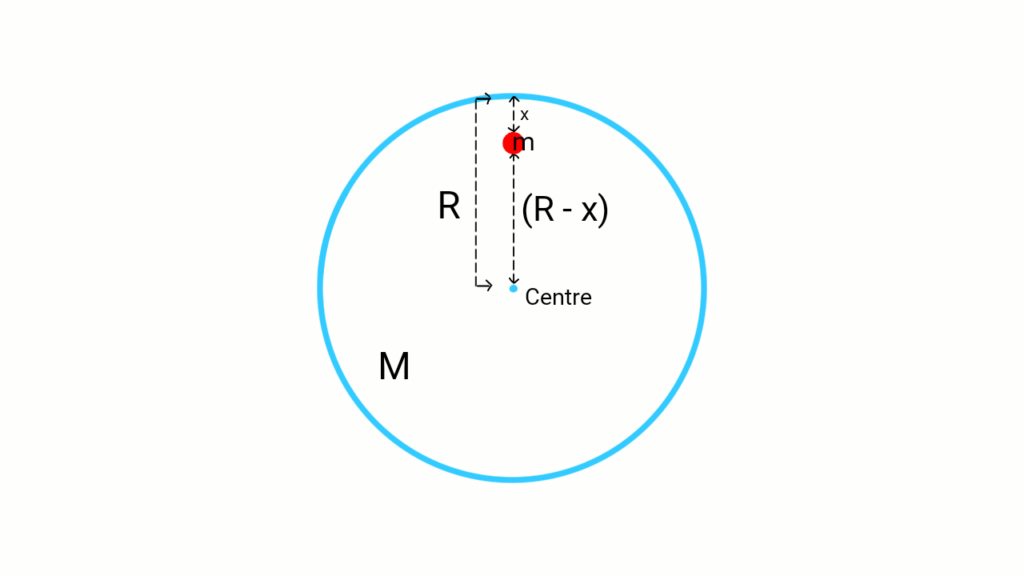
Let the mass and the radius of the earth be
Acceleration due to gravity on the surface of the earth is,
Let a body is at depth
where,
Dividing equation
In the centre of the earth,
Thus, the acceleration due to gravity at the centre of the earth is zero and if a body is kept at the centre of the earth than its weight will be zero and it will feel weightlessness.
Variation of g due to the rotation of the earth
Let the earth be a sphere of radius

But the earth is rotating. Let the earth be rotating by angular velocity

Two forces [
Variation of g in different planets and satellites
As we know that the weight of an object is the force by which the object is pulled by a planet towards its centre. According to Newton’s second law of motion,
As we know that the moon is smaller than the earth. So, its acceleration due to gravity is
The acceleration due to gravity at Jupiter is